Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams
Beam is one of the most important structural components.Beams are usually long, straight, prismatic members and always subject forces perpendicular to the axis of the beam
- A Shear Force Diagram (SFD) indicates how a force applied perpendicular to the axis (i.e., parallel to cross-section) of a beam is transmitted along the length of that beam.
- A Bending Moment Diagram (BMD) will show how the applied loads to a beam create a moment variation along the length of the beam.
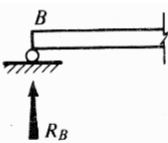
Types of Supports (a) Roller Support – resists vertical forces only

(b) Hinge support or pin connection – resists horizontal and vertical forces
- Hinge and roller supports are called as simple supports
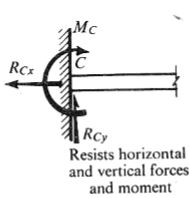
(c) Fixed support or built-in end
- The distance between two supports is known as “span”.
Types of beams : Beams are classified based on the type of supports: (1) Simply supported beam: A beam with two simple supports
(2) Cantilever beam: Beam fixed at one end and free at other
(3) Overhanging beam
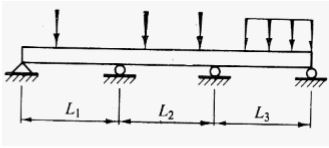
(4) Continuous beam: More than two supports
Shear Force
Shear force has a tendency to slide the surface, it acts parallel to surface.
![]()
![]()


Only for distributed load not for point load.
Bending Moment
Any moment produced by forces acting on the beam must be balance by an equal opposite moment produced by internal forces acting in beam at the section. This moment is called bending moment.

Only for distributed and concentrated load not for couple.
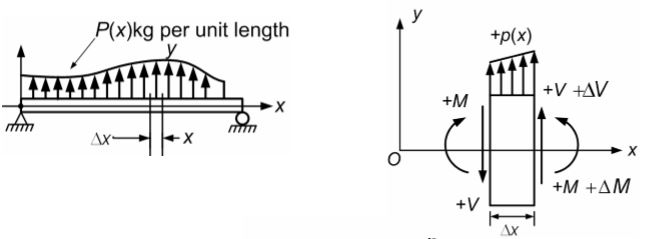
- The necessary internal forces to keep the segment of the beam in equilibrium are
Differential equations of equilibrium
Sign Conventions :
So the differential equations would be:


![]()
Statically Determinate Beam
A beam is said to be statically determinate if all its reaction components can be calculated by applying three conditions of static equilibrium i.e.,
![]()
Statically Indeterminate Beam
When the number of unknown reaction components exceeds the static conditions of equilibrium, the beam is said to be statically indeterminate.

If you are preparing for ESE/ GATE or other PSU Exams (Civil Engineering), then avail Online Classroom Program for ESE and GATE CE:
Online Classroom Program for ESE/GATE CE
You can avail of BYJU'S Exam Prep Test Series specially designed for all Civil Engineering Exams:
BYJU'S Exam Prep Test Series ESE/GATE CE
Thanks
All the Best





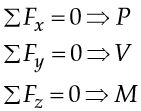
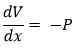






Comments
write a comment