Carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is a biogeochemical cycle where the carbon and its compounds are continuously exchanged between the three spheres of earth, i.e. hydrosphere, lithosphere and atmosphere (collectively called as biosphere).
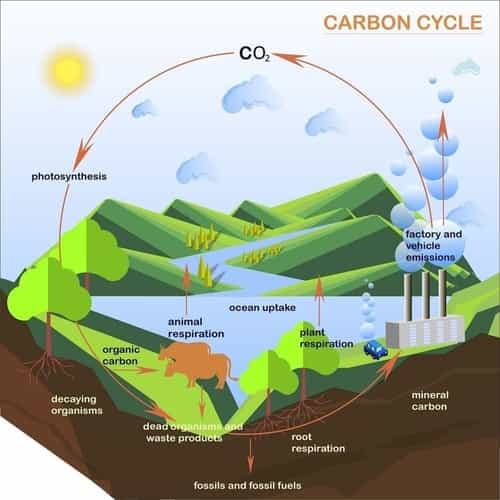
Major carbon sinks of our Earth
- In the form of organic molecules in living and dead organisms in the biosphere.
- As the gaseous carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- As organic matter in soils.
- As fossil fuels and sedimentary deposits like limestone, dolomite and chalk etc.
- As dissolved atmospheric carbon dioxide in the oceans and as calcium carbonate shells in marine organisms.
Processes involved in the Carbon Cycle
- Photosynthesis: Ecosystem gains most of their carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Most of the autotrophs have a mechanism that allows for the absorption of this gas into their cells. With the help of water and energy from solar radiation, these organisms use photosynthesis to chemically convert carbon dioxide to sugar molecules.
- Respiration: Carbon released from the ecosystem as carbon dioxide gas by the process of respiration. It involves the breakdown of the carbon-based organic molecule into carbon dioxide and some other by-products in both plants and animals.
- Detritus food chain contains a number of organisms whose primary role is to decompose organic matter. Partially decomposed organic matter becomes part of the soil carbon storage pool.
- Ultimately organic material in the soil becomes part of soil constituents, water and carbon dioxide which return to the atmosphere. This flow accounts for most of the carbon from the atmosphere but not all.
- Diffusion: Carbon dioxide enters the water by this method. Once it is dissolved in water it can remain as it is or can convert into carbonate or bicarbonate. When carbon dioxide enters the ocean, carbonic acid is formed.
- Certain organisms fix bicarbonate with calcium to form calcium carbonate. This is used to make hardbodies such as shells and corals. When such organisms die their remains accumulate as carbonate-rich deposits to the ocean floor.
Note- ocean deposits are the biggest sink of carbon on the planet.
- In the lithosphere, carbon is stored in both organic and inorganic forms. Inorganic forms include fossil fuels, coal, natural gas, oil shale and sedimentary deposits like limestone. Organic deposits are organic matter, humus etc. some carbon dioxide released from volcanoes.
To boost the preparation of all our users, we have come up with some free video (Live Class) series.
Here are the links
MP राज्य परीक्षाओं के लिए करंट अफेयर्स
मध्य प्रदेश राज्य परीक्षाओं के लिए 2000 सबसे महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न
More from us
Get Unlimited access to 45+ Mock Tests-BYJU'S Exam Prep Test Series




Comments
write a comment