Bearings: It is a mechanical element that allows relative motion of the two machine elements such as the shaft and the housing resulting in minimum friction.
Types of bearings: Based on the direction of force that acts on them, bearings are classified into two categories – radial and thrust bearings.
Radial bearings: A radial bearing supports the load, which is perpendicular to the axis of the shaft.

Thrust bearings: Thrust bearing are used to support the loads acting along the axis of the shaft.

Based on the type of friction, bearings are classified into two categories:
(i). Sliding contact bearings
(ii). Rolling contact bearings
Sliding contact bearings (Plain bearings, Journal bearings or Sleeve bearings):
- Here, the shaft surface slides over the bush surface resulting in friction and wear. Two surfaces are separated by a film of lubricating oil to reduce the friction.
- The bearing material for bush is white metal or bronze.

Rolling contact bearing(antifriction bearings):
- These bearings have the rolling elements (balls or rollers) between the surfaces having relative motion between them.
- Here, sliding friction is substituted by rolling friction.
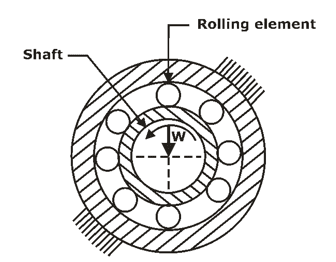
- A rolling contact bearing is made inner and outer races, a rolling component such as ball, roller or needle and a cage. The function of cage is to hold rolling elements together and to provide evenly spaces for rolling elements to avoid clustering of them around the periphery of the shaft.
- Based on the rolling element, the bearings are divided as:
(i). Ball bearings
(ii). Cylindrical roller bearings
(iii). Taper roller bearing
(iv). Needle bearing. - Based on the load direction, the bearings are also termed as radial bearing and thrust bearing.
- The types of rolling contact bearings, which are frequently used are shown in figure:

Static load carrying capacity:
- Static load is the load acting on the bearing in the stationary condition of the shaft.
- The static load carrying capacity of a bearing is the static load for which a total permanent deformation of balls and races (at the most heavily stressed point of contact) is equal to 0.0001 times of the ball diameter (D).
Dynamic load carrying capacity:
- It is expressed in terms of the number of revolutions (or hours of service at some given constant speed) completed by the bearing before the first evidence of fatigue crack in balls or races.
- It is based on the hypothesis that the inner race is rotating while the outer race is stationary.
Life of the bearing:
- The rating life of a group of an apparently identical bearings is the number of revolutions completed or exceeded before the first appearance of fatigue crack by the 90% bearings.
- The L10 life is the minimum life which 90% of the bearings will reach or exceed before fatigue failure.
Equivalent bearing load:
- In actual applications, two types of force i.e. radial and thrust, is acted in bearings. Thus, these two components acting on the bearing are converted into a single hypothetical load to fulfil the dynamic load carrying capacity conditions.
- It is the constant radial load in radial bearing (or thrust load in thrust bearings), the application of which to the bearing results in same life as the bearing will give under actual condition of forces.
Load life relationship:
The bearing life (L10) in terms of the dynamic load carrying capacity (C) and the equivalent dynamic load (P), is given by:

where, L90 = bearing Rated life (million revolutions)
C = dynamic load carrying capacity (in N)
For ball bearings: p = 3 and For roller bearings: p = 10/3.
Bearing having a probability of survival other than 90%:
The reliability is defined as:

Formula:

where, R90=0.9, and the values of a and b are constant.
Modes of lubrication in sliding contact bearings:
Lubrication is the science of friction reduction with application of a suitable substance called lubricant, between the rubbing surfaces of bodies having relative motion. The two modes of lubrication are thick – and thin film lubrication.
(i). Thick film lubrication: It is condition of lubrication in which two surfaces of the bearing in relative motion are completely separated by a film of fluid. Thick film lubrication is further has two groups:
- Hydrodynamic lubrication: A system of lubrication where load – supporting fluid film is the result of the shape and relative motion of the sliding surfaces.
- Hydrostatic lubrication: Here, the load supporting fluid film, separating the two surfaces is created by an external source such as a pump by supplying sufficient fluid under pressure.
(ii).Thin film lubrication (boundary lubrication):
- It is a lubrication condition in which the lubricant film is relatively thin and partial metal to metal contact occurs.
- The lubrication in door hinges and machine tool slides is example of thin film lubrication.
Mckee's Investigation:
There is transition from thin film lubrication to thick film lubrication as the journal starts from rest and the speed increases. This transition can be better visualized by means of a curve called BCN curve

Bearing characteristic number (BCN)- It is a dimensionless group of parameters given by:

where,
μ = absolute viscosity of the lubricant
N = journal speed
P: Unit bearing pressure (load per unit of projected area of bearing)
There are two different regions of the curve i.e. BC and CD
- For region BC, partial metal to metal contact occurs and there are partial patches of lubricant which is the state of thin film lubrication.
- The region CD shows a relatively thick film of lubricant and hydrodynamic lubrication occurs.
- Line AC divides these two modes of lubrication i.e. thin film zone (at left of AC) and the thick film zone (at right of AC).
- The coefficient of friction is minimum at C and the value of the bearing characteristic number corresponding to this minimum coefficient is known the bearing modulus (K).
- In order to avoid seizure, the bearing characteristic number ≥ 5 to 6 times of bearing modulus (K).
- If the bearing is subjected to fluctuating loads or impact conditions: bearing characteristic number ≥ 15 times of bearing modulus (K).
- The BCN curve is important because it defines the stability of hydrodynamic journal bearings and helps to visualize the transition from boundary lubrication to thick film lubrication.
Temperature rise of the lubricating oil:
- Viscosity of the lubricating oil result in the heat generation due to internal fluid friction. Thus, The frictional work is converted into heat resulting in lubricant temperature increase.
Comparison of sliding and Rolling contact bearings:
- The load carrying capacity of a hydrodynamic bearing is linearly proportional to speed. Point lying below this curve (i.e. point P1) shows that the infinite life corresponding to this load-speed.
- When the load exceeds and reaching at point P2 will result in breaking of fluid film and thus causing metal to metal contact.

- In hydrostatic bearings, the load capacity is independent of speed. For a given set of load and speed conditions, the rolling contact bearings result in finite life .
- Rolling contact bearings have poor damping capacity and thus they are vulnerable to shock loads. Hydrodynamic bearings are better suited for these conditions, which occur in connecting rod and crankshaft applications.
- Rolling contact bearings have need of considerable radial space, while hydrodynamic bearings require more axial space.
- In case of rolling contact bearings, the axes of the journal and bearing are collinear. In hydrodynamic bearings, the journal motion is eccentric with respect to the bearing and the eccentricity is function of the load and speed.
- Due to metal to metal contact, rolling contact bearings generate more noise as compared to hydrodynamic bearings.
- The cost of hydrodynamic bearing is much more than that of rolling contact bearing due to additional accessories, like pump, filter and pipelines.
- The maintenance cost is more in hydrodynamic bearings while rolling contact bearings are cheaper.
You can avail of BYJU’S Exam Prep Online classroom program for all AE & JE Exams:
BYJU’S Exam Prep Online Classroom Program for AE & JE Exams (12+ Structured LIVE Courses)
You can avail of BYJU’S Exam Prep Test series specially designed for all AE & JE Exams:
BYJU’S Exam Prep Test Series AE & JE Get Unlimited Access to all (160+ Mock Tests)
Thanks
Team BYJU’S Exam Prep
Download BYJU’S Exam Prep APP, for the best Exam Preparation, Free Mock tests, Live Classes.





Comments
write a comment